Trace formatting
Articles
- The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics Elaine Mardis Trends in Genetics 2008
- As Users Demand Paired-End Sequencing, 454, Illumina, and ABI Work On New Kits
- Sequence Format Descriptions(EMBL)
- ismb2007Poster.pdf
- Smith_Rennes_2007.pdf
- GenomeAnalyzer_SpecSheet.pdf
- Assembly and Alignment Algorithms for Next-Gen Sequence Data
- Sequencing of natural strains of Arabidopsis thaliana with short reads (Illumina)
- Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing
- Advanced sequencing technologies and their wider impact in microbiology
- Emerging technologies in DNA sequencing
- Lander Waterman
- Whole-genome re-sequencing
- [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/picrender.fcgi?artid=1871613&blobtype=pdf Whole-Genome Sequencing and Assembly with High-
Throughput, Short-Read Technologies]
Technologies
Latest Technology Summary
Technology 454 Illumina Solid
seq-by-synthesis seq-by-synthesis ABI Company 454(Roche) Illumina Location Brandford,CT SanDiego,CA Latest GS FLX, Titanium reagents Genome Analyzer II SOLID 3
Throughput 500M/run 1G/run 20G/run RunTime 10hr 3days ReadLen 500bp 36 35 InsertLen 3K 100-200bp 600-10K
Accuracy 99.94%
Q20(99%accuracy) 400bp 34bp
Cost $3K/run 60K/3G
$400/4M bacterial genome(25-30X)
Problems homopolimers
Sanger
454
- Pyrosequencing
- 454_Life_Sciences wikipedia
Anomalies:
* homopolymer lengths can be shorter than real * substitutions less likely than in traditional methodssingle base insertions * carry forward events usually near but not adjacent to homopolymers
GS20
* 1.6M total wells * 450K detactable wells * 200K usable wells
Accuracy: * published per-base accuracy of a Roche GS20 is only 96%. * Mitch Sogin paper * 99.5% accuracy rate in unassembled sequences * identified several factors that can be used to remove a small percentage of low-quality reads, improving the accuracy to 99.75% or better => better quality than Sanger sequencing * The error rate, defined as the number of errors (miscalled bases plus inserted and deleted bases) divided by the total number of expected bases, was 0.49% * 36% insertions, 27% delitions, 21% N's, 16% substitutions * A to G and T to C, were more frequent than other mismatches * reverse transitions, G to A and C to T, were not that frequent * Nearly 70% of the homopolymer extensions were A/T * errors were evenly distributed along the length of the reference sequences, they were not evenly distributed
among reads: 82% had no errors, 93% had no more than a single error, and 96% had no more than 2 errors.
* A small number of reads, fewer than 2%, contained a disproportionate number of errors that account for nearly 50% of the miscalls for the entire dataset * Avg quality is 25; in homopolymers can drop as low as 5 * Reads much longer than avg length had more errors * strong correlation between the presence of ambiguous base calls and other errors in a read * The presence of even a single ambiguous base in a read correlates strongly with the presence of other errors * Primer errors also correlated with errors
GS FLX
GS FLX with Titanium reagents
* up to 500M/run * reads up to 500bp
Get info from .sff files:
$ sffinfo -h
Usage: sffinfo [options...] [- | sfffile] [accno...]
Options:
-a or -accno Output just the accessions
-s or -seq Output just the sequences
-q or -qual Output just the quality scores
-f or -flow Output just the flowgrams
-t or -tab Output the seq/qual/flow as tab-delimited lines
-n or -notrim Output the untrimmed sequence or quality scores
-m or -mft Output the manifest text
un-paired reads
paired ends
Features:
* approximately 84-nucleotide DNA fragments * have a ~ 44-mer linker sequence in the middle * flanked by a ~ 20-mer sequence on each side. * The two flanking 20-mers are segments of DNA that were originally located approximately 2.5 (3?) kb apart in the genome of interest. * The ordering and orienting of contigs generates scaffolds which provide a high-quality draft sequence of the genome.
Linker(palindrome) : GTTGGAACCGAAAGGGTTTGAATTCAAACCCTTTCGGTTCCAAC Check for linker : sffinfo -s *.sff | ~/bin/fasta2tab.pl | grep GTTGGAACCGAAAGGGTTTGAATTCAAACCCTTTCGGTTCCAAC 12345678901234567890123456789012345678901234 GTTGGAACCGAAAGGGTTTGAATTCAAACCCTTTCGGTTCCAAC
GTTGGAACCGA AAGGGTTTGAA TTCAAACCCTT TCGGTTCCAAC
Anomalies:
* the linker can appear (tandem,completely/partially) more than once * some reads end up in linker (partial) * some reads don't contain the linker at all * some reads are cloning vector
Links:
1_paired_end.pdf
File location:
/fs/szdata/454p/
Illumina
- Sequencing by Synthesis
- Platforms:
* Genome Analyzer (GA) * Genome Analyzer II : faster, higher tput * Future: 10GB/run 50bp reads * Future: 20GB/run 100bp reads
Data sets:
Strep suis Solexa data set for download at Sanger Staphylococcus aureus strain MW2 (edena paper) NCBI Solexa example data set Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas syringae NCBI SRA
Applications:
* Gene Expression * ChIPSeq (hight throughput) * Re-sequencing * mRNA sequencing
Software:
Staden & Io_lib * IO_LIB package /fs/sz-user-supported/common/packages/io_lib-1.11-x86_64/bin/ * STADEN package /fs/sz-user-supported/common/packages/staden-src-1-7-0/distrib/unix-rel-1-7-0/linux-bin MAQ Sanger assembler FASTQ sequence format
Illumina 1G :
* ~40 Million DNA sequencing reactions * about 36 hours for a run * each sequence is up to 36 bases long * insert len=~200bp
Illumina Genome Analyzer II:
* up to 51 bp * mate-pairs: opposite directions, slight overlap (insert size is less than 200bp "advertised") * on the SRA mate-pairs are joined; when downloaded only one read is shown. What about the mate pair?
SRA: set of 4 files
*_seq.txt : lane,run, well(x,y) sequence *_prb.txt : max quality from each group of 4 values is taken as quality *_sig2.txt : lane,run, well(x,y); max signal from each group of 4 values corresponds to max quality *_qhg.txt : lane,run, well(x,y); some encoded info?
# *_seq.txt 5 1 1269 1795 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA # _prb.txt 40 -40 -40 -40 40 -40 -40 -40 ... # _sig2.txt <== 5 1 1269 1795 2594.0 2367.0 -10.0 -96.0 ...
Qualities:
Range : -5..40 Avg : ~25, depending on the data set
Fastq format
Example:
1 lane of Solexa reads: 10,959 READS; all are 36 bp $ /fs/sz-user-supported/common/packages/io_lib-x86_64/bin/solexa2srf s_8_0100_seq.txt ; mv traces.srf s_8_0100.srf $ /fs/sz-user-supported/common/packages/io_lib-x86_64/bin/srf2fastq s_8_0100.srf > s_8_0100.fastq @s_8_100_293_551 CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCACC + IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII @s_8_100_35_698 TATATGATTGACAATATAAAAATATGAGTATAAAAT + IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII4/:I @s_8_100_880_947 TTATTATCTTTATTGACGTACCTCTAGAAGACCCAA + IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII;>1 ...
Edge effect: N's have quality -14
$ cat s_8_0100_seq.txt | sort -nk3 -nk4 8 100 0 37 ......AT.AT...TAATCAATA..GA.GAAG.... ... 8 100 1003 959 AGTC.......T.C.........GT.........AA
$ more traces.qual ... >s_8_100_0_37 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 25 13 -14 25 25 -14 -14 -14 25 25 25 25 22 25 25 25 25 -14 -14 25 25 -14 25 -11 25 14 -14 -14 -14 -14 ... >s_8_100_1003_959 25 25 25 25 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 25 -14 25 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 25 -10 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 -14 8 25 ...
# bioperl script to convrt seq formats
$ seqconvert.PLS --from fastq --to fasta < s_8_0100.fastq
# get fastq qualities
$ more *fastq | grep -A 1 "^+" | grep -v ^+ | grep -v -- ^-- | perl -ane '@F=split //,$F[0]; foreach (@F) { $n=ord($_)-33; print $n," ";} print "\n";'
# convert Solexa format (maq fq_all2std.pl script) $ fq_all2std.pl seqprb2std s_5_0001_seq.txt s_5_0001_prb.txt > s_5_001.fastq $ fq_all2std.pl fq2fa s_5_001.fastq > s_5_001.seq
SOLiD
- ABI SOLiD
- article
- Tools & Data Sets
- color space (0123) => base space (ACGT)
- .csfsta file : in color space; start with a known base (usually T)
Example:
Ecoli_F3.csfasta >600_50_31_F3 T2222002113300322132112231 >600_50_63_F3 T2330133212130133221033110
Ecoli_F3_QV.qual >600_50_31_F3 15 20 14 11 25 20 17 21 16 9 15 12 21 8 2 10 15 5 3 5 10 6 2 4 4 >600_50_63_F3 5 13 9 23 5 9 8 4 6 4 5 4 7 6 10 7 7 5 13 11 5 8 2 7 6
Ecoli_R3.csfasta >600_51_85_R3 G0331332123123330101312331 >600_51_178_R3 G1111033111110111101111111
Ecoli_R3_QV.qual >600_51_85_R3 10 13 16 15 11 17 6 13 10 9 15 8 13 10 12 11 8 5 3 6 12 8 11 6 14 >600_51_178_R3 2 2 2 5 8 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 2 3 7 4 3 4 5 4 2 2 5 6 17
- low error rate (higher accuracy than Illumina)
- 2008: 4G run, read_len=35bp; insert=3Kbp (old)
- 2009: 9G run, read_len=50bp;
- SOLiD™ 3 System generates (Oct 1 2008)
- over 20 gigabases
- mate-paired libraries with insert sizes ranging from 600 bp up to 10 kbp
- human genome for less than $60,000.
- uniform bases quality
- accuracy greater than 99.94%
- because of double base interogation & high cvg, qualities can be "discarded"
Alignment matrix
A C G T A 0 1 2 3 C 1 0 3 2 G 2 3 0 1 T 3 2 1 0
Examples:
AA is encoded as 0 CG is encoded as 3 AACG is encoded as 0 1 3
Features of Color space:
* Color space data are self-complementary
Example:
Base A G C T C G T C G T G C A G
Color space 2 3 2 2 3 1 2 3 1 1 3 1 2
Complemented
Base T C G A G C A G C A C G T C
Color space 2 3 2 2 3 1 2 3 1 1 3 1 2
* Two-Base Encoding and Error Recognition 1 change: measuring error multiple changes starting at a certain point: SNP
Example:
Reference 2 3 2 2 3 1 2 3 1 1 3 1 2
Observed 2 3 2 2 0 1 2 3 1 1 3 1 2
Data Sets:
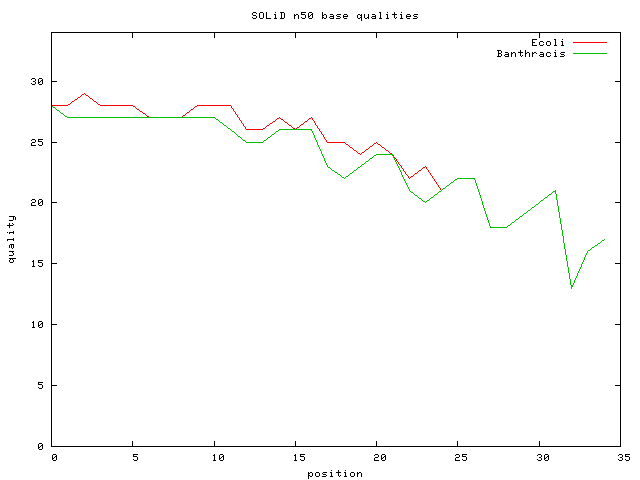
- E.Coli DH10B Mate-Pair Data Set ~ 56M 25bp paired reads =~ 1G bp ; 56M*25/4.6M => 300X cvg
- E.Coli DH10B Mate-Pair Data SubSet ~ 1.9M 25bp paired reads ; 10.17X cvg; avg inset is 2Kbp
- Bacillus anthracis 27M 35 bp unmated reads => 187X cvg
Helicos
Pacific Biosystems
Visigen
Download
Genbank
- Bioperl scripts:
bp_fetch.pl net::genbank:NC_005810.1 > NC_005810.1 bp_fetch.pl net::genbank:NC_005810 > NC_005810 bp_fetch.pl net::genbank:45439865 > 45439865
TA
SRA
Format
TA
- Sanger:
tarchive2amos -o Ba Ba.seq # TA FTP tarchive2amos -o Ba -tracedir traces/ # TA querytrace_db tarchive2amos -o Ba -assembly assembly/ASSEMBLY.xml -tracedir traces/ # AA
SRA
- Solexa mated:
seq2amos.pl -n solexap -m 100 -s 20 -fs solexa_f.fasta -rs solexa_f.fasta > solexap.afg seq2amos.pl -n solexap -m 100 -s 20 -fs solexa_f.fasta -fq solexa_f.qual -rs solexa_r.fasta -rq solexa_r.qual > solexap.afg seq2amos.pl -n solexap -m 100 -s 20 -fs solexa_f*.fasta -rs solexa_r*.fasta > solexap.afg
- Solexa unmated:
seq2amos.pl -n solexa -fs solexa.fasta > solexa.afg
- 454 mated:
seq2amos.pl -n 454p -m 3000 -s 300 -fs 454.seq > 454p.afg
- 454 unmated:
seq2amos.pl -n 454 -fs 454.seq > 454.afg
Convestion
- Readseq
~/bin//readseq.sh -f Fasta -o prefix.fasta prefix.embl
- Bioperl
bp_sreformat.pl -i prefix.embl -o prefix.fasta -if EMBL -of Fasta
- AMOS:
amos2frg [-i infile] [-o outfile] amos2sq [-i] infile [-o outprefix] => outprefix.seq outprefix.qual
Read Mapping Software
BFAST
- need to e-mail to author to get the code
BLAT
- BLAT—The BLAST-Like Alignment Tool, Genome Research 2002
- FAQ
- Can align any type of reads
- Can do nt:aa translation
- Command: blat
blat -noHead -t=dna -q=dna -tileSize=10 -stepSize=3 Pa.1con Pa.seq Pa.blat
MAQ *
- Maq Sourceforge
- Maq Poster from Sanger
- Illumina-Solexa/AB-SOLiD , not 454 or capillary reads
- Uses FASTQ format
- Command: maq map ...
- does ungapped alignment on unpaired reads
SOLEXA maq.pl easyrun -d . ref.1con reads.fastq
SOLID solid2fastq.pl reads_ shortname maq fastq2bfq shortname.fastq shortname.bfq maq fasta2csfa ref.fasta > ref.csfa maq fasta2bfa ref.csfa ref.csbfa maq fasta2bfa ref.fasta ref.bfa maq map -c aln.cs.map ref.csbfa shortname.bfq 2> aln.log maq csmap2nt aln.nt.map ref.bfa aln.cs.map maq assemble cns.cns ref.bfa aln.nt.map 2> cns.log
RMAP
- RMAP : designed for Illumina-Solexa
- Command: rmap
rmap -m 3 -w 33 -c Pa.1con Pa.seq -o Pa.rmap
SHRiMP
- Web site
- Commands: rmapper-cs , rmapper-ls, ...
SeqMap
- SeqMap developed at Stanford
- allows up to five mixed substitutions and inserted/deleted nucleotides in the mapping
- allows sequences to contain N’s, and to have unequal lengths
./seqmap Usage: seqmap <number of mismatches> <probe FASTA file name> <transcript FASTA file name> <output file name> [options] Parameters: <number of mismatches> maximum edit distance allowed <probe FASTA file name> probe/tag/read sequences <transcript FASTA file name> reference sequences <output file name> name of the output file ...
SHORE
SOAP *
- Web site (China)
- Formatofoutput
- SOAP: short oligonucleotide alignment program, Bioinformatics Jan 2008
- Commands: soap, soap.contig, soap_dealign, soap.huge, soap.short
- can use qualities, do read trimming, use pair ends, RNA alignments
soap -v 5 -d Pa.1con -a Pa.seq -o Pa.soap
SOCS
- Web site
- ABI color space
socs socs.pref more socs.pref Req.fa Seq_F3.csfasta Seq_F3_QV.qual out_prefix 2 1000 2 false true 0
SOLiD
SSAHA
- Web site(Sanger)
- Focused on exact, nearly exact matches
- Does not find all the exact matches???
- Example: Solexa 33bp ~30% of reads are not found
ZOOM
Genome Resequencing
- The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing (J.Watson's genome) Nature April 2008
- J.Watson's genome (supplementary info)
Links
Data
Solexa
- Strep suis Solexa at Sanger 36bp, ~49X coverage
- Staphylococcus aureus strain MW2 (edena paper) 35bp, ~47X coverage
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 33bp, ~43X coverage
- Pseudomonas syringae: 32bp, ~31X coverage
- 1000 Genomes (June 14th 2008): 47bp
Accession #Runs Instrument Center Study [Individual] SRA000303 41 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer BI 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878 SRA000304 49 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer BI 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12891 SRA000305 56 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer BI 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12892 SRA000307 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA10851 SRA000308 2 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA11993 SRA000309 3 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA11995 SRA000310 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12006 SRA000311 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12044 SRA000312 2 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12156 SRA000313 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12414 SRA000314 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12776 SRA000315 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12828 SRA000316 12 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878 SRA000317 8 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12891 SRA000318 14 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12892 SRA000319 1 Solexa 1G Genome Analyzer SC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12004
June 14th 2008: Sept 19th 2008
SRA001100 23 Illumina Genome Analyzer BGI 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA19240 ... SRA002029 1 Illumina Genome Analyzer II WUGSC 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA19239
/fs/szdata/Solexa/1000genomes
- Example SRR001113.seq :
7,058,926 47 bp sequences 2,402,398 contain at least 1 '.'
454
- 1000 Genomes
June 14th 2008
Accession #Runs Instrument Center Study [Individual] SRA000302 121 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878 SRA001032 2 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878 SRA001036 1 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12812 SRA001094 1 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878
June 14th 2008: Sept 19th 2008
SRA001037 2 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 1 NA12812 ... SRA001819 1 454 GS FLX BCM 1000Genomes Project Pilot 2 NA12878
Refseq
- /fs/szdata/genomes/human_ncbi_build36/ NCBI build36.1 May 2006 (Current build is 36.3 March 2008)
- /fs/szdata/genomes/human_celera_2001_Orig/
Alignments
Whole genomes alignments
- BLAT
- BLASTZ, Post-processing long pairwise alignments article. decom program
- LAGAN
- MUMMER
- AVID