SecureShell: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
This will give you access to a terminal on any one of the [[OpenLAB]] servers. Note that by default you will not have access to applications that require X11 to run. | This will give you access to a terminal on any one of the [[OpenLAB]] servers. Note that by default you will not have access to applications that require X11 to run. | ||
All UMIACS-supported Windows hosts are installed with [http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ PuTTY]. If you are using a self-supported machine, you can either download and install PuTTY yourself, or if you are running a [https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/windows-10-enterprise-and-education currently supported version of Windows 10], you can install the OpenSSH client natively in Windows by following Microsoft's instructions [https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/openssh/openssh_install_firstuse here]. | All UMIACS-supported Windows hosts are installed with [http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ PuTTY]. If you are using a self-supported machine, you can either download and install PuTTY yourself, or if you are running a [https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/windows-10-enterprise-and-education currently supported version of Windows 10], you can install the OpenSSH client natively in Windows by following Microsoft's instructions [https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/openssh/openssh_install_firstuse here]. Only the client is needed and not the server. | ||
==X11 Forwarding== | ==X11 Forwarding== | ||
Revision as of 21:00, 17 February 2021
Secure Shell (or SSH) is a network protocol allowing two computers to exchange data securely over an insecure network. By default, use of SSH brings the user to a terminal, but the protocol can be used for other types of data transfer such as SFTP and SCP.
Connecting to an SSH Server
Under Linux and macOS, the following command from a terminal will connect a client computer to the UMIACS OpenLAB.
# ssh bkirz@openlab.umiacs.umd.edu
This will give you access to a terminal on any one of the OpenLAB servers. Note that by default you will not have access to applications that require X11 to run.
All UMIACS-supported Windows hosts are installed with PuTTY. If you are using a self-supported machine, you can either download and install PuTTY yourself, or if you are running a currently supported version of Windows 10, you can install the OpenSSH client natively in Windows by following Microsoft's instructions here. Only the client is needed and not the server.
X11 Forwarding
By default, SSH only gives the user shell access to a host. Enabling X11 Forwarding allows users to run applications with Graphical User Interfaces.
Under Linux and macOS, the following command from a terminal will connect a client computer to the UMIACS OpenLAB using X11 Forwarding. Please note that under macOS, xQuartz is required on the client machine to forward X sessions from the remote session.
# ssh -Y bkirz@openlab.umiacs.umd.edu
Under Windows, you will need to forward X through VcXsrv or Xming.
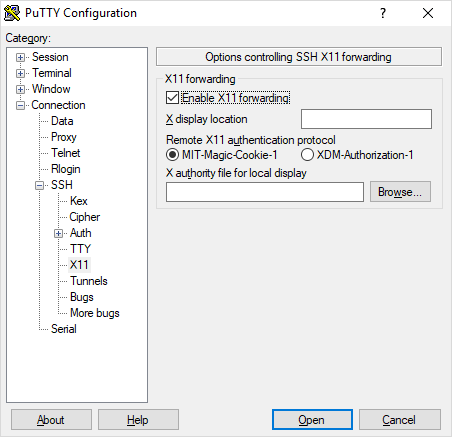
First, enable X forwarding on PuTTY. The option is under Connection > SSH > X11, shown below.
Next, configure your SSH session and click open to start a SSH session.
After this has been done, every time you want to use X forwarding, you need to make sure VcXsrv or Xming has been started (it will appear in your task tray) through the start menu programs. Now, you will be able to use Xwindow programs from your ssh client.
SSH Tunneling
You can tunnel one or more ports through an SSH connection such that your packets will look like they are coming from the host you are tunneling to. This is helpful for services that you would be normally blocked by a firewall.
Please see the SecureShellTunneling page for more information.
SSH Keys (and Passwordless SSH)
SSH can utilize public key encryption to authenticate and authorize users. This can be considered more secure especially if you secure your private key with a pass-phrase. The keys themselves are not susceptible to brute force attacks like normal passwords over SSH are.
Please see the SSH/Keys page for more information.
Verify remote host SSH fingerprint
The SSH protocol relies on host keys to verify the identify of a given host. Each host as a unique key for the various different protocols supported.
When connecting to a remove host for the first time, or when the remote host's local host key configuration has changed, you may see the following prompt:
$ ssh sabobbin@openlab The authenticity of host 'openlab (128.8.132.247)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 25:83:aa:df:f5:ad:5f:08:c9:8a:a3:5d:97:8b:48:1f. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
It is considered best practice to verify the key fingerprint with the actual key of the host. UMIACS maintains a reference of SSH key fingerprints available at the following link: https://gitlab.umiacs.umd.edu/staff/ssh-fingerprints/blob/master/fingerprints
It is important to note that each key type has a different fingerprint. Depending on your local configuration, your client may prefer a specific type of key. The following commands can be used to determine the fingerprint of a given key type on a remote host:
$ ssh-keyscan -t rsa openlab.umiacs.umd.edu > key # openlab.umiacs.umd.edu:22 SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.0 $ ssh-keygen -l -E md5 -f key 2048 MD5:25:83:aa:df:f5:ad:5f:08:c9:8a:a3:5d:97:8b:48:1f openlab.umiacs.umd.edu (RSA)
If you have any questions, or notice a discrepancy, please submit a request to staff@umiacs.umd.edu.
Windows / PuTTY Verification
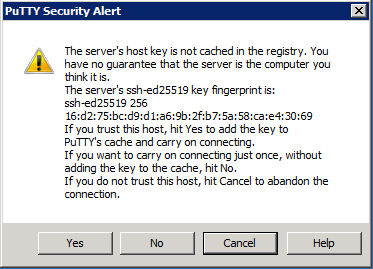
If you use PuTTY to connect to remote hosts, the prompt will be similar to the following:
If the host key reported by PuTTY matches the Documented entry for that host, it is safe to click 'yes'. If they do not match, please report the issue to staff@umiacs.umd.edu.
Other Platforms
Long Running Processes
If you are dealing with a long running process that is inhibiting your ability to work regularly, you may want to run your processes inside a screen on the host that you're connecting to. This way, if the connection is dropped for any reason the screen session will automatically detach on the host and will continue running so that you can reattach it at a later time when you've connected again. Please see our documentation on GNU Screen for more information.