SecureShellTunneling
Port Forwarding
When you want to just forward a specific port locally to a remote port.
- This example will create a local port 9999 that will be forwarded to the remote host webbserver.umiacs.umd.edu and its port 8000 through the host openlab.umiacs.umd.edu.
ssh -NfL 9999:webserver.umiacs.umd.edu:8000 openlab.umiacs.umd.edu - This example will create a local port 13389 that will be forwarded to a remote host that is running a RDP client like Windows through the host openlab.umiacs.umd.edu
ssh -L 13389:my-desktop.pc.umiacs.umd.edu:3389 openlab.umiacs.umd.edu - The following example outlines how to use SSH tunnel for printing to the UMIACS CUPS server.
ssh $<USERNAME>@openlab.umiacs.umd.edu -T -N -L 3631:print.umiacs.umd.edu:631 - Once the tunnel is established you can follow the normal Printing instructions substitution 'print.umiacs.umd.edu' for 'localhost:3631', or print via the a command such as the following:
lpr -H 127.0.0.1:3631 -P $<PRINTER NAME> $<FILENAME>
SOCKS Proxy
SSH can also tunnel all traffic coming into a certain port through a SOCKS v5 proxy. Many browsers and some operating systems can be setup to then connect to this proxy to allow them again to look like they are coming from the host name you specify in your SSH command.
- ssh -ND 7777 openlab.umiacs.umd.edu
Please note: when you configure proxy settings for a browser (or your whole operating system) all the traffic for that browser (or the OS) will be sent through the proxy. This can have performance implications.
Port Forwarding with PuTTY
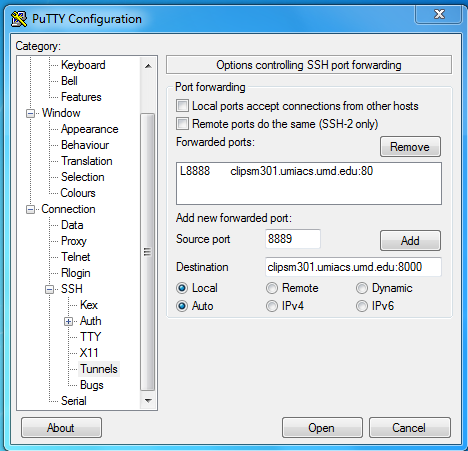
Windows users can achieve the same types of tunnels using PuTTY or a similar SSH client. In PuTTY, the port forwarding configuration dialogue can be found under "Connection>SSH>Tunnels".
This example will create a local port 8889 that is attached to the remote host clipsm301.umiacs.umd.edu on its port 8000.
Socks Proxy with PuTTY
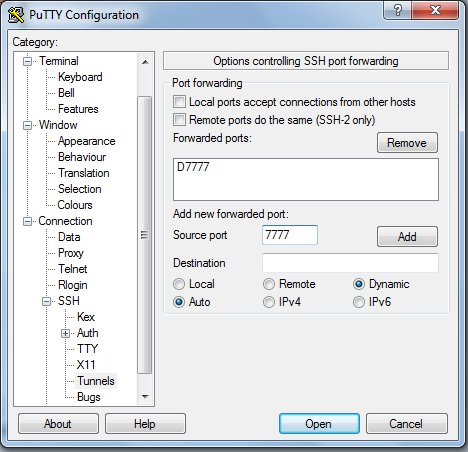
Windows users can tunnel traffic coming into a certain port through a SOCKS v5 proxy by using PuTTY or a similar SSH client. Many browsers and some operating systems can be setup to connect to this proxy to allow them to look like they are coming from the host name you specify.
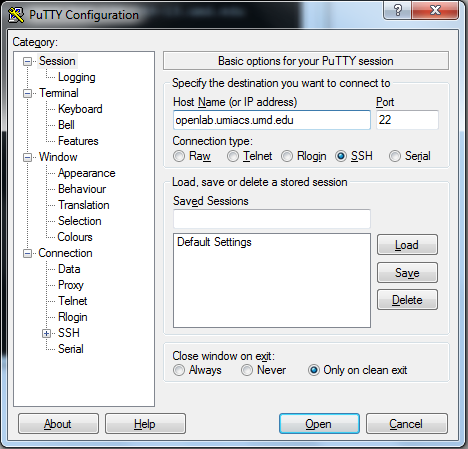
In PuTTY under "Sessions" set the Host Name:
Then under "Connection>SSH>Tunnels" enter a port number and set the type of forwarding to "Dynamic" and press add:
Click Open and log into the host. As long as this PuTTY window is open and you are logged in, you can use the SOCKS proxy.
Please note that when you configure proxy settings for a browser or your whole operating system, all the traffic for that browser or your OS will be sent through the proxy. This can have performance implications.
Example: SOCKS proxy, Browser configuration
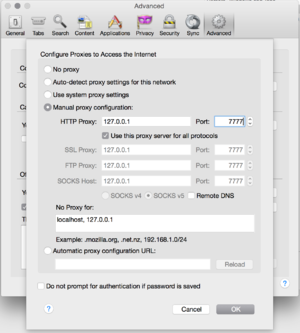
There are too many variations here to cover them all, but they all follow the same general pattern and the following example should be generally applicable. We'll use Firefox for this example. Screenshots are from FF 37.0.2
- Under
Preferences > Advanced > Network > Connection > Settings... - choose
Manually proxy configuration:, - enter
127.0.0.1for the proxy - enter the port you chose earlier for dynamic forwarding (7777 in the example above.)
- Check
Use this proxy server for all protocols, and then click OK.
NOTE: this will continue to send all browser traffic through your SSH tunnel until the configuration is reverted. The SSH connection must be established for traffic to pass through to the destination network. Firefox has a very useful plugin called "FoxyProxy" that allows conditional proxies to be set up, if you're interested in adding some intelligence/complexity to your proxy configuration.