Adobe Illustrator: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
This image trace will scan your image and produce it as a Scalable Vector Graphic (SVG) which means it can be resized to any size and keep its quality. This SVG is whats needed for the UCP to be able to cut. Without this SVG the image will not be printed. | This image trace will scan your image and produce it as a Scalable Vector Graphic (SVG) which means it can be resized to any size and keep its quality. This SVG is whats needed for the UCP to be able to cut. Without this SVG the image will not be printed. | ||
Each of these image traces | Each of these image traces are used in different situations to produce a different outcome: | ||
*'''High/Low Fidelity Photo''': Used for tracing actual images. High is for high quality and low is for lower quality images (Try both to see which is better) | |||
*'''3/6/16 Colors''' | |||
*'''Shades of Grey''' | |||
*'''Black and White Logo''' | |||
*'''Silhouettes''' | |||
These are not all the possible options but the most useful ones. Feel free to try the others and figure out their uses. You can also keep switching between all of the options to see which is the best fit for your image. | |||
=== Outlining an Image === | === Outlining an Image === | ||
| Line 26: | Line 32: | ||
#*If you are in CMYK mode or vector cuts don't seem to be showing up as vector cuts in the UCP then check this setting. | #*If you are in CMYK mode or vector cuts don't seem to be showing up as vector cuts in the UCP then check this setting. | ||
#In order to cut out an image you need to image trace it. See [[#Using Image Trace | Using Image Trace]] for more help. | #In order to cut out an image you need to image trace it. See [[#Using Image Trace | Using Image Trace]] for more help. | ||
#When rastering images onto glass and clear acrylic, do not try and use intricate pictures with many colors. | |||
#*Glass and clear material doesn't differ much depending on how deep the cut is. Normally try and make it a silhouette or black and white logo and it will cut much nicer. | |||
Revision as of 17:35, 25 December 2019
Adobe Illustrator is a graphic design application used to create Universal Control Panel (UCP, laser cutter printer program) compatible files that can be printed. Adobe illustrator is not the only file that can create files compatible for printing but it is the program that is default installed on the two computers in the prototyping room hooked up to the cutters. From adobe illustrator you can print to the UCP by printing and setting the printer as VLS. If you have another program you use to create graphics, you can export the graphic as an image and import it into Adobe to print on the computers in the room.
Adobe Illustrator is available for all UMD students on terpware with a valid student account. You can then create designs on your own computer and just bring it in to be printed.
If you would like anything added to the wiki please comment in the discussion tab at the top or inform a manager.
Adobe Basics
The easiest way to get started is clicking create new and either using one of the preset templates for size or go to art & illustration and making a large canvas by changing the size to some large number bigger than you need like 15 inches by 15 inches (Make sure you change the units from points to inches).
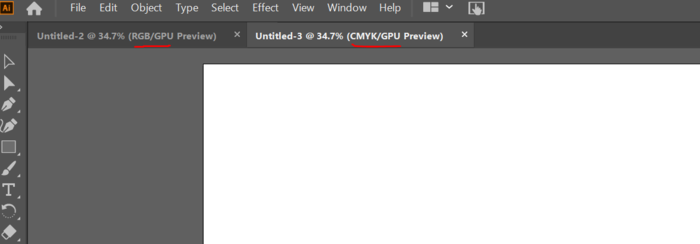
Make sure you are in RGB mode under "Advanced Options" because if you aren't then you won't be able to make a full blue line for vector cutting (To change, go to File->Document Color Mode).
Importing and Editing Images
Images can be imported into Adobe by dragging the picture from your computer onto the canvas or copy pasting the image from the internet. All images that are entered will default be rastered because the colors are not absolutely red or blue like cutting needs to be.
Using Image Trace
The image entered is normally something like a PNG or JPG or similar picture. Adobe Illustrator needs it to be an SVG file to be able to print to the printer as a raster. This can be done by clicking the image and going to the image properties and clicking "Image Trace".
This image trace will scan your image and produce it as a Scalable Vector Graphic (SVG) which means it can be resized to any size and keep its quality. This SVG is whats needed for the UCP to be able to cut. Without this SVG the image will not be printed. Each of these image traces are used in different situations to produce a different outcome:
- High/Low Fidelity Photo: Used for tracing actual images. High is for high quality and low is for lower quality images (Try both to see which is better)
- 3/6/16 Colors
- Shades of Grey
- Black and White Logo
- Silhouettes
These are not all the possible options but the most useful ones. Feel free to try the others and figure out their uses. You can also keep switching between all of the options to see which is the best fit for your image.
Outlining an Image
Adobe Tips
- Make sure when you are creating the new page for design, that the advanced option is set to RGB mode or else you won't be able to make the colors for vector cutting.
- If you are in CMYK mode or vector cuts don't seem to be showing up as vector cuts in the UCP then check this setting.
- In order to cut out an image you need to image trace it. See Using Image Trace for more help.
- When rastering images onto glass and clear acrylic, do not try and use intricate pictures with many colors.
- Glass and clear material doesn't differ much depending on how deep the cut is. Normally try and make it a silhouette or black and white logo and it will cut much nicer.