Ace:Validating Witness and Tokens: Difference between revisions
From Adapt
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===Issuing Tokens=== | ===Issuing Tokens=== | ||
Tokens are issued to clients after they submit a request. The request contains a hash to secure and a file name. All the hashes for a given time are gathered together and a summary value(CSI) is generated and stored on the IMS. After the round completes and a CSI is generated, clients are given a token that contains enough information to recalculate the CSI for its round. Comparing the recalculated CSI to the CSI stored on the IMS will let clients prove their hashes and tokens are valid. | |||
==Validating Tokens and Hashes== | ==Validating Tokens and Hashes== | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 18 September 2008
Overview
ACE offers a two tiered method for ensuring the validity of hashes. The first tier involved calculating a summary value (CSI) for a set of hashes given to the IMS. These CSIs are composed of all hashes for a given time period (round). This CSI can be used to validate any hash submitted during its round. The second tier involves periodically publishing a witness value that is calculated from all CSI values issues during the previous day.
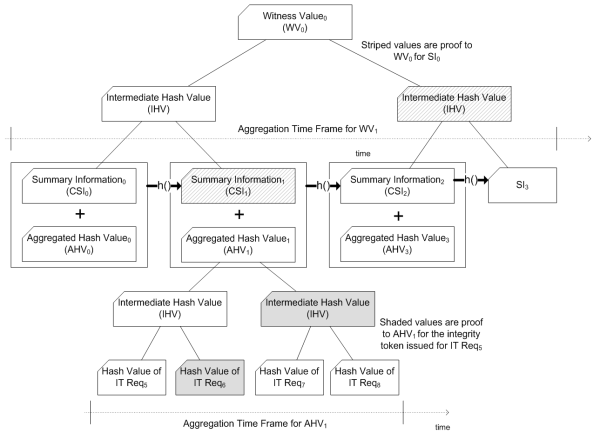
Issuing Tokens
Tokens are issued to clients after they submit a request. The request contains a hash to secure and a file name. All the hashes for a given time are gathered together and a summary value(CSI) is generated and stored on the IMS. After the round completes and a CSI is generated, clients are given a token that contains enough information to recalculate the CSI for its round. Comparing the recalculated CSI to the CSI stored on the IMS will let clients prove their hashes and tokens are valid.
Validating Tokens and Hashes
Token Overview
A token contains all information needed to validate a hash. A sample token is shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<token xmlns="http://umiacs.umd.edu/adapt/ace/token/1.0">
<token-class>SHA-256-0</token-class>
<digest-service>SHA-256</digest-service>
<name>/state/myfile.txt</name>
<round-id>319782</round-id>
<time-stamp>2008-09-16T14:57:27.936-0400</time-stamp>
<proof>
<element index="0">
<hash>7957e058645f953f8e2d11c919414adffab7df12df3e7902eb446b02a40ac908</hash>
</element>
<element index="1">
<hash>9287c2e19f715a67dcb59da8a724084b448dd9382668f347338f1ce20f435872</hash>
</element>
<element index="2">
<hash>e9cc9417014a43e29870f60504cdbe3c49ba9472b4481bb2ff5f7a68cef147bb</hash>
<hash>73384002a2fd512874801fb62e1defbb1902668f04d8a96d6cb90b703d16a506</hash>
</element>
<element index="1">
<hash>d312e4551a3d3ee6d695d96b8851f3ad1574096305f18d4f052fe853bfe14482</hash>
</element>
</proof>
</token>
- token-class:
- digest-service:
- name: name of the file this token refers to. This was supplied by the client in a token request.
- round-id: The ID of the round this token was issued in. This is used to request a CSI from the IMS.
- time-stamp: the timestamp for this round
- proof: tree elements that can be used to locally generate a CSI given a files hash.