Webarc:Search and Access Strategies: Difference between revisions
From Adapt
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Background == | |||
* The Web has become the main publication medium world-wide, covering almost every facet of human activity. However, the Web is an ephemeral medium. | |||
* Web archives offer unique opportunities for knowledge discovery due to the richness of their contents extending over significant periods of time. | |||
* We need effective and scalable access strategies for web archives covering significant temporal spans. | |||
== Goals == | |||
* An effective technology to explore and search for information in a web archive. The technology must enable effective information exploration and discovery. | |||
* A framework that produces ranking and evaluation of archived web contents within a temporal context as required by the user. | |||
* Methods to determine the relevance of a group of web objects within the temporal context. A group can consist of a series of temporally-contiguous versions of a single URL, or of web objects archived within some time span. | |||
* A framework that allows effective search using keywords and time spans for large scale web archives. | |||
== Existing Access Methods == | |||
* Chronological Listing | |||
[[Image:dup_nw_pages.png|320px]][[Image:dup_gw_pages.png|320px]] | |||
* Directory | |||
[[Image:dup_nw_pages.png|320px]][[Image:dup_gw_pages.png|320px]] | |||
* Text-Search | |||
[[Image:dup_nw_pages.png|320px]][[Image:dup_gw_pages.png|320px]] | |||
* Hybrid | |||
[[Image:dup_nw_pages.png|320px]][[Image:dup_gw_pages.png|320px]] | |||
== Problems With Existing Methods == | |||
* Inefficient handling of time-constrained search. | |||
[[Image:dup_nw_pages.png|320px]][[Image:dup_gw_pages.png|320px]] | |||
* Ineffective delivery of search results | |||
Inadequate relevancy scoring. | |||
Scoring is performed over the entire history. | |||
Ungrouped search results. | |||
URL is not unique in web archives – time dependent. | |||
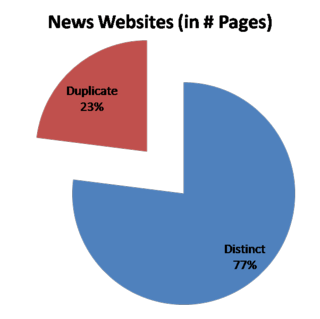
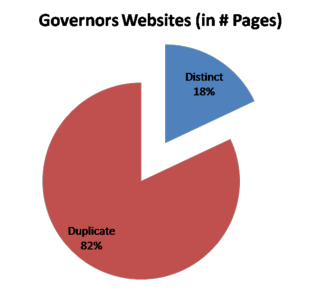
Considering different versions of the same URL tend to have similar contents, It is highly likely to have the first result page “polluted’ by multiple versions of the same URL. | |||
Users can want to focus more on a specific time-period within the results. | |||
Lack of a group-scoring methodology. | |||
What group to show on the top is not clear without a group-scoring methodology. | |||
== Overview of Our Approach == | |||
* Efficient time-constrained search by maintaining separate inverted lists for a given time window. Click here for details. | |||
* Scoring within a temporal context by computing term weights as a function of time. Click here for details. | |||
* Grouping similar search results, while scoring search results as a group. Click here and here for details. | |||
== Basic Techniques == | |||
== Scoring within a Temporal Context == | |||
== Search User Interface == | |||
== Grouping Search Results == | |||
== Group-wide Scoring == | |||
== Publication == | |||
Song, S. and JaJa, J., Archiving Temporal Web Information: Organization of Web Contents for Fast Access and Compact Storage:UMIACS-TR-2008-08. 2008, University of Maryland Institute for Advanced Computer Studies. [[media:temporal-web-archiving-final-umiacs-tr-2008-08.pdf|pdf]] | |||
Revision as of 19:04, 12 May 2009
Background
- The Web has become the main publication medium world-wide, covering almost every facet of human activity. However, the Web is an ephemeral medium.
- Web archives offer unique opportunities for knowledge discovery due to the richness of their contents extending over significant periods of time.
- We need effective and scalable access strategies for web archives covering significant temporal spans.
Goals
- An effective technology to explore and search for information in a web archive. The technology must enable effective information exploration and discovery.
- A framework that produces ranking and evaluation of archived web contents within a temporal context as required by the user.
- Methods to determine the relevance of a group of web objects within the temporal context. A group can consist of a series of temporally-contiguous versions of a single URL, or of web objects archived within some time span.
- A framework that allows effective search using keywords and time spans for large scale web archives.
Existing Access Methods
- Chronological Listing
- Directory
- Text-Search
- Hybrid
Problems With Existing Methods
- Inefficient handling of time-constrained search.
- Ineffective delivery of search results
Inadequate relevancy scoring. Scoring is performed over the entire history. Ungrouped search results. URL is not unique in web archives – time dependent. Considering different versions of the same URL tend to have similar contents, It is highly likely to have the first result page “polluted’ by multiple versions of the same URL. Users can want to focus more on a specific time-period within the results. Lack of a group-scoring methodology. What group to show on the top is not clear without a group-scoring methodology.
Overview of Our Approach
- Efficient time-constrained search by maintaining separate inverted lists for a given time window. Click here for details.
- Scoring within a temporal context by computing term weights as a function of time. Click here for details.
- Grouping similar search results, while scoring search results as a group. Click here and here for details.
Basic Techniques
Scoring within a Temporal Context
Search User Interface
Grouping Search Results
Group-wide Scoring
Publication
Song, S. and JaJa, J., Archiving Temporal Web Information: Organization of Web Contents for Fast Access and Compact Storage:UMIACS-TR-2008-08. 2008, University of Maryland Institute for Advanced Computer Studies. pdf